First published in June 2017, updated June 2021
Playing and spending time outdoors is such an important part of childhood but it is crucial that children are protected and safe in the sun.
Increased vulnerability
Compared with adults, children’s skin is much more vulnerable to the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
Young children’s skin has lower concentrations of the protective skin pigment melanin.
The outer layer of children’s skin is also thinner than those of adults. This allows UV radiation to penetrate more deeply through the layers of the skin.
Childhood: a critical time for sun protection
Childhood is a ‘critical period’ during which skin cancer risk can be increased in later life. Research has indicated that having ‘ever’ experienced a sunburn in childhood, nearly doubles the risk of melanoma of the skin in adulthood.
It all adds up!
Sun damage is cumulative. Preventing overexposure to UV radiation and sunburn in childhood reduces the risk of sun damage, and skin cancer in later life.
Enjoy the sun safely: keep babies and children out of direct sunlight
Babies and young children should stay in the shade as much as possible. Although shade can reduce UV radiation by 50% or more, other forms of sun protection should also be used to shield against exposure from reflected UV radiation, from surfaces such as concrete or sand.
In other words, it is possible to get sunburn under an umbrella if you have no additional protection.
Protect your child’s skin with:
- Loose-fitting comfortable clothing made from tightly-woven fabrics.
- A broad brimmed or legionnaire style hat to protect the face, back of the neck and ears. Soft hats are available for babies that allow freedom of movement and easily crease or crumple if they rest their head.
- Child-size UV protective sunglasses.
Remember shade for prams and buggy/pushchairs. When ‘out and about’ ensure children do not get overheated and drink plenty of fluids.
If possible, plan your day’s activities in advance to reduce your children’s exposure to the sun, particularly between 11am and 3pm when UV rays are strongest. Remember use of sunscreens should not be regarded as a means of increasing the duration of sun exposure.
Sunscreens
Sunscreens should not be your main method of sun protection – remember to seek shade and wear sun protective clothing.
Sunscreens are not usually recommended for babies younger than 6 months as they have very absorptive skin. Cover with appropriate protective clothing and a hat. Apply sunscreen on small exposed areas only when sun avoidance is impossible.
For babies and children older than 6 months, apply a broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) 50+, with high UVA protection (and ideally water-resistant sunscreen, particularly if swimming) on any exposed areas of skin, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Reapply generously and evenly every two hours. Physical (inorganic) sunscreens that reflect UV radiation away from the skin (e.g. those containing ingredients zinc oxide or titanium dioxide), or sunscreens specifically made for babies or toddlers may cause less irritation to sensitive skin. More detailed information about SPF, UVA protection and correct quantities to use here.
Did you know…?
- It is possible to burn on a cloudy day.
- Commonly neglected areas of the body regarding sunscreen application include the lips and the ears.
- Sunscreens do go out of date. It is best not to hang on to last year’s product.
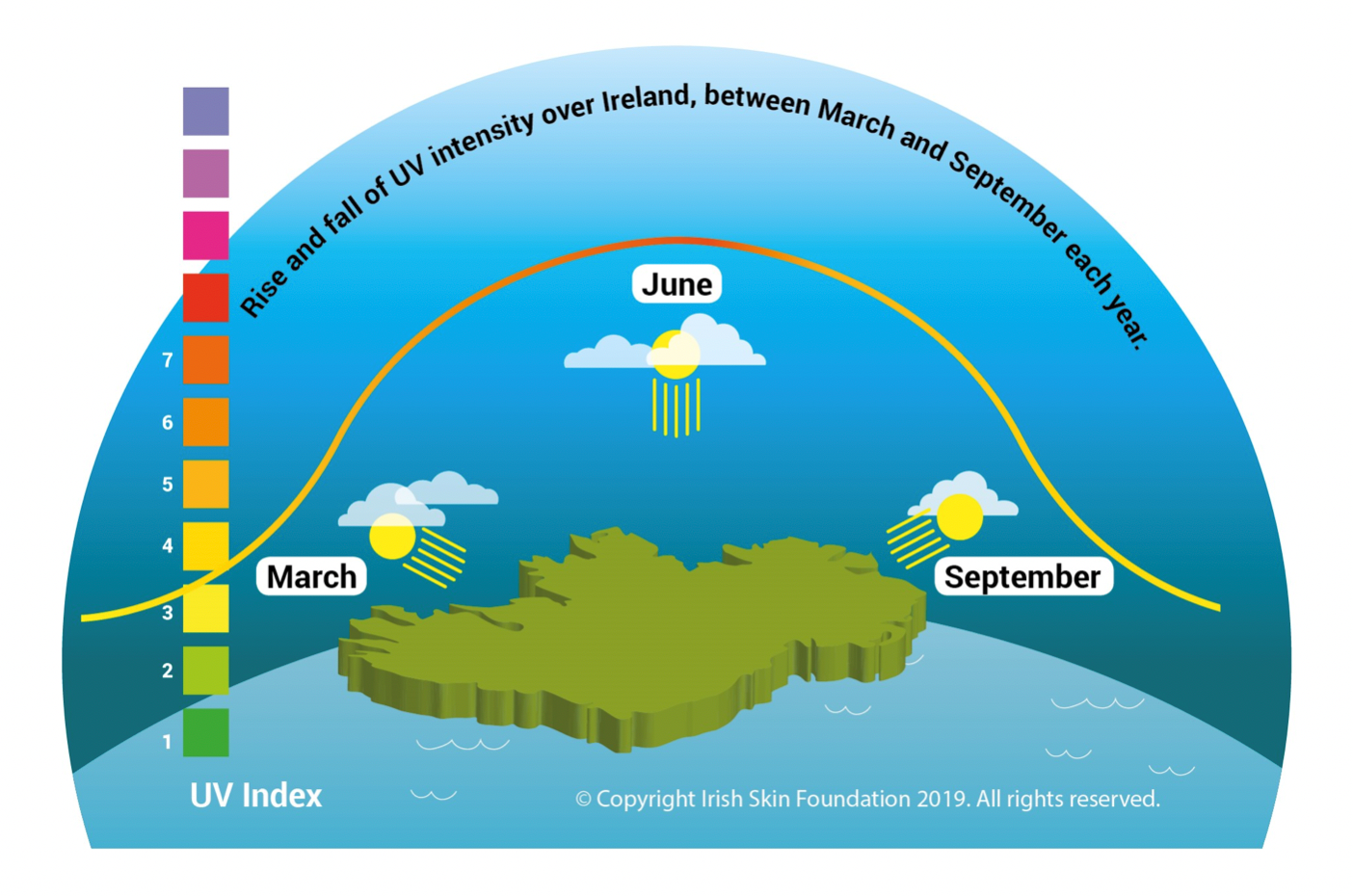
Know the UV index
The UV index is a scale that measures the UV radiation level at the surface of the Earth, and gives an indication of the potential for skin damage, particularly sunburn. The UV index ranges from zero upwards – the higher the number, the greater the risk.

In Ireland, make sun protection part of your daily routine especially from April-September, when the intensity of sunburn producing UV is greatest, even when it is cloudy!
Stay safe by limiting time in the sun when UV is strongest, typically between the hours of 11:00am-3:00pm.
Remember the SunSmart 5 ‘Ss’: Slip, Slop, Slap, Seek, Slide
- Slip on clothing: Cover skin as much as possible e.g. wear long sleeves, collared t-shirts, clothes made from close-woven material that does not allow sunlight through.
- Slop on broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30+ for adults and 50+ for children, with high UVA protection, and water resistant. Reapply regularly.
- Slap on a hat with a wide brim: Protect your face, ears and neck.
- Seek shade e.g. sit in cover of trees to avoid direct sunlight and use a sunshade on your buggy or pram. Keep babies and children out of direct sunlight.
- Slide on sunglasses with UV protection: Guard your eyes from harm.
Next article: Clouds, water, glass: surprising things that solar UV can pass through
For more information on how to Protect & Inspect™ against Melanoma Skin Cancer visit our information and resources page.












